One Big App (High-Performance) #
You have an application and want to increase its performance and throughput by distributing it over multiple nodes.Setup #
Let’s say we have three nodes:
node001node002node003
Our app consists of two two stateless services (http and api), and
one stateful service (db).
Stateful Service #
We will just pin our db service to one node in our example. Most databases
and storage engines can run in more than one instance for increased throughput,
but how to do that is specific to each database.
Stateless Services #
We want to start:
- 1 of each
apiservice on each node, i.e. 1x3=3 replicas - 2 of each
httpservice on each node, i.e. 2x3=6 replicas
In practice, finding the fastest or highest-throughput number of replicas (especially per-node replicas) can take some trial and error.
Stack.yml #
Putting it all together:
| |
In detail:
replicas: the number of (overall) replicasmax_replicas_per_node: the maximum number of replicas per node- placement constraint
node.hostname == node001: pinning of thedbservice to node001
`max_replicas_per_node` restricts the actual number of started services, even if `replicas` is higher. That is, in our example we could have set `replicas: 7` for `http` and it would have still only started 6 (2 `max_replicas_per_node` x 3 nodes). The rest of the replicas are basically "waiting" for a node. They will display as `pending` in the Quantum UI: 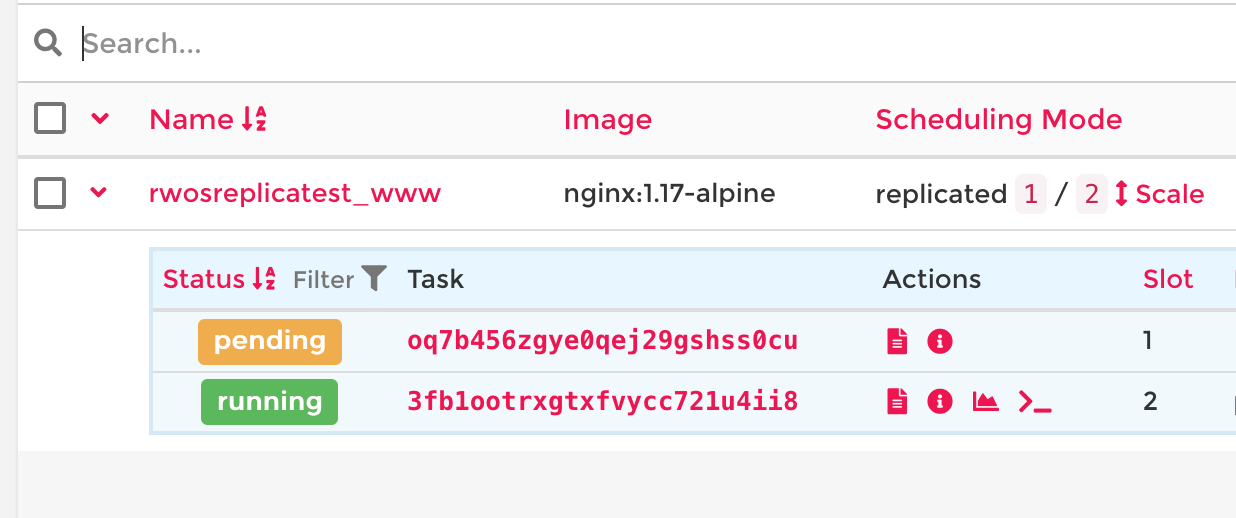 The individual task view will give the reason for the `pending` state: